Introduction
In a time when AI and digital tools are common, how can we get students more interested in learning and help them learn more? The answer might be in non-textual AI assignments.
These cutting-edge educational tools offer a new way to learn that goes beyond traditional text-based learning. They get students involved in a more dynamic and interactive learning process.
This blog post will talk about how non-textual AI assignments can change things. By using technology in ways that require students to be creative, think critically, and work together, these assignments can greatly improve student engagement and learning results.
We will talk about how these assignments, which can be anything from multimedia projects to interactive simulations, can help students learn in different ways, provide a better understanding, and get them ready for the digital world.
Let us look at how non-textual AI assignments can change the game in education and help solve the main problem of how to keep students interested and help them learn faster.
The Challenge of AI in Education
Pervasiveness of AI Tools and Their Limitations
Using AI-powered tools in education has changed the game, but it also brings its own problems. More and more people are using AI technologies, especially big language models like OpenAI’s GPT-3.
Some of these improvements are Automatic Essay Writing (AEW) tools that can write whole essays in answer to prompts.
While these tools can sometimes make simple content, it’s getting harder and harder to tell the difference between work that was written by AI and work that was written by students. This makes it hard to figure out how much kids really know and what they can contribute.
AI chatbots, another AI tool widely used in education, have shown a significant impact on learning outcomes. They are particularly effective in providing immediate assistance, enhancing knowledge retention, and improving the educational experience. However, their effect on student motivation remains debatable.
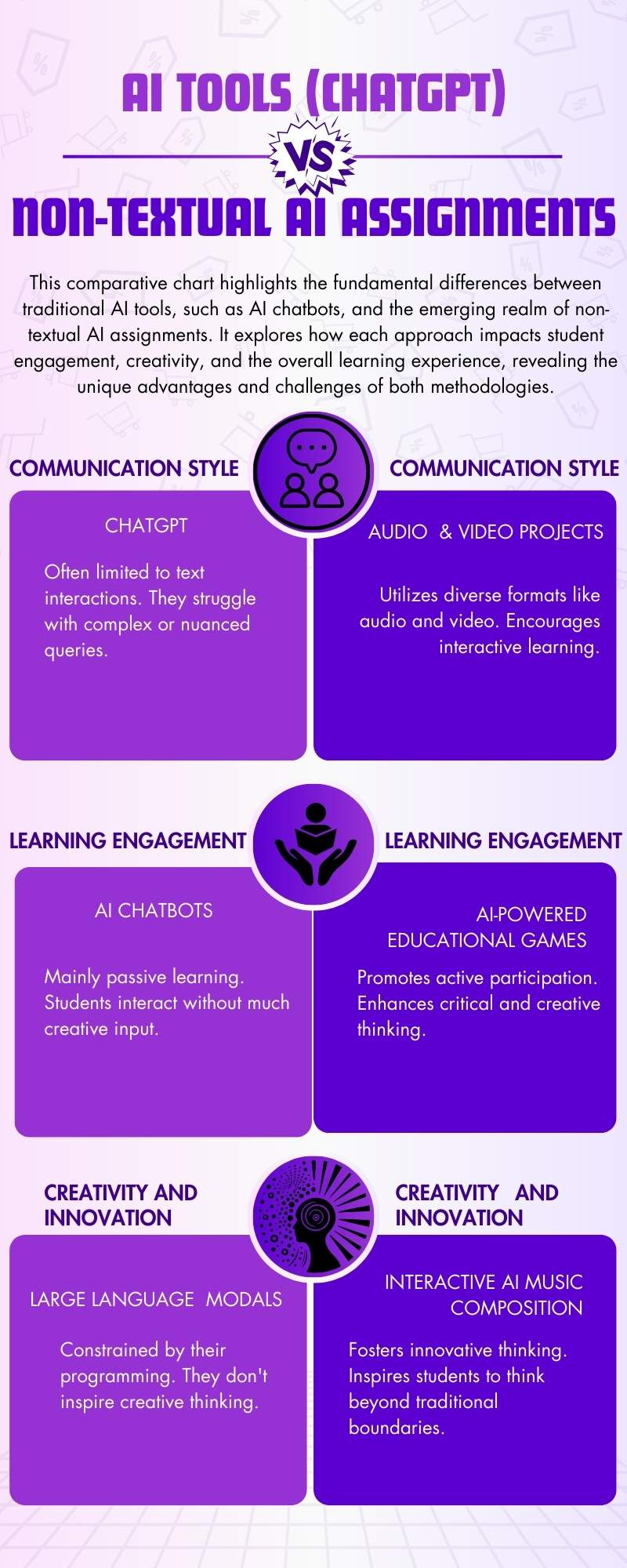
While some studies report an increase in student motivation through chatbot use, others find no significant improvement in this area. This discrepancy highlights the need for a nuanced understanding of how AI tools affect different aspects of student learning and engagement.
Despite their potential, these tools also face limitations. There is concern regarding the irrational use of technology and the challenges education systems face in harnessing its full potential.
AI chatbots, for example, vary in their applications, from teaching various subjects to offering personalized learning experiences. However, challenges in chatbot development, such as ensuring the relevance and accuracy of the information provided, remain.
In summary, while AI tools have revolutionized certain aspects of education, they also bring to light significant challenges. The limitations in assessing AI-generated content and the mixed results regarding their impact on student motivation and engagement underscore the need for innovative approaches in education.
This sets the stage for exploring non-textual AI assignments as a solution to these challenges, leveraging AI’s potential while addressing its limitations.
The Potential of Non-Textual Assignments
Exploring Beyond Text
The use of non-textual assignments in education is emerging as a powerful tool to enhance learning experiences and outcomes. Moving away from traditional text-based assessments, non-textual assignments encourage a broader range of skills and knowledge applications.
The Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning at Indiana University Bloomington suggests that assignments beyond traditional exams or research papers can provide more accurate reflections of the kind of thinking and problem-solving skills educators aim to develop in their students.
Advantages of Non-Textual Elements
Non-textual elements in educational settings offer unique advantages. They can bring important clarity to multi-layered research problems, reveal patterns and trends within data, and condense complex information into more digestible formats.
For instance, visual aids such as charts, graphs, and photographs can help to humanize a research problem, making it more relatable and understandable to students. This approach is particularly effective in disciplines that are inherently visual or practical, such as the sciences and arts, where concepts can be better understood through visual representation rather than textual descriptions.
Enhancing Learning through Visual Representation
The incorporation of non-textual elements like diagrams, maps, and infographics facilitates a deeper understanding of complex issues. These elements can simplify and highlight key information, aiding in the comprehension of intricate subjects.
For example, a study on environmental issues might use GIS maps to visually represent data, providing students with a clearer understanding of the impact on different communities.
This method not only enhances the learning process but also encourages students to engage more deeply with the material.
The Role of Non-Textual Assignments in Diverse Learning Environments
Non-textual assignments are particularly beneficial in diverse learning environments. They cater to different learning styles, making education more inclusive. Students who might struggle with traditional text-based learning can find new ways to engage and excel through non-textual means.
By embracing a variety of learning formats, educators can create a more equitable and effective learning environment.
In summary, non-textual assignments offer a dynamic and inclusive approach to learning, accommodating various learning styles and enhancing comprehension of complex topics.
Their use in education is a testament to the evolving nature of teaching methodologies, which focus on developing a range of skills and knowledge applications in students.
Types of Non-Textual Assignments
Podcasts and Their Collaborative Nature
Podcasts have emerged as an engaging and dynamic non-textual AI assignment, fostering creativity and collaboration among students. In educational settings, podcasts can serve various purposes, from building community to practicing presentation skills. They offer students a platform to express themselves through multiple media forms, including spoken word, music, and sound effects.
A study on student-produced podcasts in interprofessional learning showed that podcasts were favored as an assignment tool, highlighting their appeal in collaborative settings. These assignments can bring together students from various disciplines, promoting interdisciplinarity and the sharing of diverse perspectives.
Creating a podcast involves not just recording but also scripting, editing, and considering the listener’s experience. Tools like Audacity and GarageBand are often used for editing, making the process accessible and manageable for students. Podcasts, being a linear medium, require students to carefully plan the sequence and pacing of their content, enhancing their organizational and storytelling skills.
Video Assignments and Their Demands for Creative Expression
Video assignments are another form of non-textual AI assignment that demand high levels of creative expression. These assignments allow students to convey their understanding of a subject through visuals, sound, and storytelling.
The process of creating a video—from planning and scripting to shooting and editing—engages students in a multifaceted learning experience.
Videos can range from documentary-style presentations to creative storytelling, offering students a platform to explore various aspects of a topic. They encourage students to delve deeper into the subject matter, engaging not only their analytical skills but also their creativity and technical abilities.
Interactive Projects Like Mind Maps and Their Emphasis on Visual Learning
Interactive projects such as mind maps emphasize visual learning and are particularly effective in engaging students who are visual learners. These assignments encourage students to organize and visually represent information, fostering a deeper understanding of the relationships between concepts.
Mind maps can be used in various subjects to help students brainstorm, plan essays, or summarize information. These visual tools make complex information more accessible and understandable, allowing students to see the bigger picture and how different pieces of information connect.
In conclusion, non-textual AI assignments like podcasts, video projects, and interactive mind maps offer diverse and engaging ways for students to learn and express their understanding.
These assignments cater to different learning styles and encourage creativity, collaboration, and critical thinking, making them valuable tools in the modern educational landscape.

Enhancing Student Engagement with Non-Textual Assignments
Deeper Student Involvement Through Non-Textual Assignments
Non-textual assignments, by their nature, encourage active participation and a deeper level of engagement from students. These assignments typically involve applying knowledge to real-world situations, thus making learning more relevant and engaging.
For example, case studies are an effective approach where students tackle real-world problems, enhancing their problem-solving skills and engagement with the subject matter.
According to Edutopia, this approach resembles project-based learning but places more emphasis on reflection during the problem-solving process.
Case Studies of Successful Non-Textual Assignments
These case studies illustrate how non-textual assignments can transform the learning experience, making it more engaging and applicable to real-life scenarios.
By focusing on problem-solving, collaboration, and applying knowledge in practical contexts, these assignments have proven to be effective tools for enhancing student engagement and learning outcomes.
Improving Learning Outcomes with Non-Textual Assignments
Non-textual assignments have shown significant effectiveness in enhancing learning outcomes in various educational settings.
Research indicates that the use of multimedia and non-textual elements in teaching, especially in ESL and EFL contexts, has led to improved engagement, interaction, and participation among learners.
Studies have consistently endorsed the positive impact of these methods in language learning environments, highlighting how they can support better comprehension and performance.
For example, integrating audio-visual elements or videos in language classrooms as part of a dual teaching method has been shown to provide an impactful approach for learners.

This method combines traditional and multimedia methods, thus catering to a wider range of learning preferences and styles.
In addition to language learning, the use of non-textual elements across various disciplines has contributed to a more dynamic and engaging learning environment.
These elements serve not only as supplementary materials but also as core components of the teaching content, enhancing students’ comprehension and performance in various subjects.
The research underscores the value of incorporating non-textual assignments in education, demonstrating their role in improving learning outcomes and student engagement.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Non-Textual Assignments
Digital Skills Gap in Educators
A key challenge in implementing non-textual assignments is the digital skills gap among educators. Many teachers, despite being exposed to digital competency frameworks, find it challenging to integrate these skills systematically into their teaching practices.
This gap is especially evident in the context of rapid shifts to digital modalities, as highlighted during the pandemic situation. The development of digital skills among teachers is crucial but often lacks coherence and systemic integration in both in-service and pre-service education.
Assessment and Grading Challenges
Traditional higher education assessment practices often focus on alphabetic or numeric grading systems, leaving little room for alternative assessment methods like non-textual assignments.
Implementing these non-traditional strategies requires a rethinking of assessment practices, shifting focus from compliance and authoritarian teaching to a more engaging and student-centered approach.
This shift can be a significant hurdle, especially in institutions where traditional assessment methods are deeply entrenched.
Strategies for Overcoming These Challenges
Developing Information Literacy and ICT Self-Efficacy
Addressing the digital skills gap requires a focus on developing both information literacy and ICT self-efficacy among educators.
This involves not just equipping them with specific ICT skills but also integrating these skills with pedagogical content knowledge and teaching strategies.
The development of information search and evaluation abilities is critical, as these skills directly impact teachers’ confidence and effectiveness in using digital tools.
Innovative Assessment Practices
To overcome the challenges in assessment, educators can explore non-traditional assessment practices such as mediated office hours, mastery learning, and ungrading strategies.
| Assessment Practice | Benefits for Students | Benefits for Teachers |
| Mediated office hours | Provides personalized feedback and guidance Encourages self-reflection and goal-setting Fosters student-teacher rapport and trust | Allows for deeper understanding of student needs and progress Enhances communication and feedback skills Reduces grading workload and stress |
| Mastery learning | Ensures mastery of essential skills and knowledge Promotes self-paced and differentiated learning Increases motivation and confidence | Supports formative assessment and feedback Aligns assessment with learning objectives and standards Improves student achievement and retention |
| Ungrading | Shifts focus from grades to learning Empowers students to take ownership and responsibility of their learning Enhances intrinsic motivation and creativity | Challenges traditional assessment norms and practices Engages students in co-creating assessment criteria and processes Fosters a culture of trust and collaboration |
These approaches focus on enhancing the learning process and providing individualized student support. Implementing these methods involves redefining quality group work and end products and possibly involving learners in building these definitions.
To sum up, using non-textual assignments can be hard at first, especially for teachers who don’t know much about technology and traditional ways of testing. But these problems can be solved by focusing on information literacy and coming up with new ways to test students.
Conclusion: The Transformative Power of Non-Textual AI Assignments in Education
As we’ve explored throughout this post, non-textual AI assignments hold remarkable potential to revolutionize the educational landscape. These innovative tools extend beyond traditional text-based learning, engaging students in dynamic, interactive processes that cater to diverse learning styles.
We’ve seen how they foster deeper understanding, encourage creativity, and enhance collaboration.
From podcasts and videos to interactive projects like mind maps, non-textual AI assignments have proven effective in enhancing student engagement and learning outcomes.
They offer educators a unique way to address the challenges posed by traditional teaching methods and the growing influence of AI in education.
By incorporating non-textual AI assignments into the curriculum, educators can open new pathways of learning and discovery for their students. We encourage educators to experiment with these methods, adapt them to their teaching context, and share their experiences.
Let’s continue the conversation on how non-textual AI assignments can further transform learning and teaching in our digital age.









Recent Comments