Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet.
IoT has been transforming various industries and sectors, such as healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, and transportation. But what about education?
How can IoT be applied to the classroom, and what are the benefits for students and teachers?
In this blog post, we will explore the concept and features of an IoT classroom, a learning environment that leverages IoT devices and solutions to enhance the learning experience for students and teachers.
We will discuss the advantages of IoT classroom for improving learning outcomes, engagement, personalization, collaboration, and feedback.
We will also provide some examples of IoT devices used in the classroom, such as smart boards, wearables, RFID tags, and sensors.
Finally, we will address some challenges and limitations of the IoT classroom, such as cost, security, privacy, and ethical issues, and provide some best practices and tips for implementing and managing the IoT classroom.
If you are interested in learning more about how the Internet of Things classroom can transform the future of education, read on and join the conversation.
IoT Classroom: What Is It and Why Is It Important?
The IoT classroom is a learning environment that leverages IoT devices and solutions to enhance the learning experience for students and teachers.
The smart classroom can be seen as a subset of smart classroom, which is a broader term that encompasses various technologies and innovations that support learning and teaching, such as artificial intelligence, augmented reality, virtual reality, cloud computing, and big data.
The IoT classroom has several benefits for students and teachers, such as:

Enhancing learning outcomes
A connected learning environment can help students achieve better academic performance by providing personalized and adaptive learning, real-time feedback, and interactive and immersive learning experiences.
The IoT classroom can also help teachers improve their instructional strategies and assessment methods by providing data-driven insights and recommendations.
Increasing engagement
Smart educational devices can help students stay motivated and interested in learning by providing gamified and fun learning activities, such as quizzes, puzzles, and simulations.
The IoT classroom can also help teachers create more engaging and relevant learning content and scenarios by using IoT devices to connect to the real world and real problems.
Facilitating personalization
The IoT classroom can help students learn at their own pace and style by providing customized and differentiated learning paths, content, and support.
The IoT classroom can also help teachers cater to the diverse needs and preferences of students by providing individualized and flexible learning options and interventions.
Promoting collaboration
The IoT classroom can help students work together and learn from each other by providing collaborative and social learning platforms, such as online forums, chats, and wikis.
The IoT classroom can also help teachers foster a collaborative and inclusive learning culture by providing tools and opportunities for communication, feedback, and peer review.
Improving feedback
The IoT classroom can help students monitor and improve their learning progress and performance by providing instant and continuous feedback, such as scores, badges, and dashboards.
The IoT classroom can also help teachers provide timely and effective feedback to students by using IoT devices to track and analyze student behavior, engagement, and achievement.
There is ample evidence that the IoT classroom can have a positive impact on education.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global IoT in education market size is expected to grow from USD 9.8 billion in 2021 to USD 25.5 billion by 2026, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.0%.
Moreover, according to a survey by Extreme Networks, 46% of K–12 and higher education organizations have deployed IoT devices on their campuses, and 71% of them have seen improved student outcomes as a result.
However, the IoT classroom is not without challenges and limitations. Some of the major issues that the IoT classroom faces are:

Cost
IoT classrooms require a significant investment in infrastructure, devices, software, and maintenance, which may not be affordable or feasible for many schools and educators, especially in developing countries and rural areas.
Security
The IoT classroom poses a high risk of cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access, which may compromise the privacy and safety of students and teachers, as well as the integrity and quality of learning and teaching.
Privacy
The IoT classroom involves the collection, processing, and sharing of large amounts of personal and sensitive data, such as biometric, behavioral, and academic data, which may raise ethical and legal concerns and require strict compliance with data protection laws and regulations.
Ethics
The IoT classroom may have unintended and undesirable consequences, such as creating digital divides, biases, and inequalities, undermining human agency and autonomy, and affecting social and emotional development and well-being.
Therefore, the IoT classroom requires careful planning, implementation, and management, as well as awareness, education, and regulation, to ensure that it is used in a responsible, ethical, and beneficial way.
IoT Classroom: How Does It Work and What Are the Best Practices?
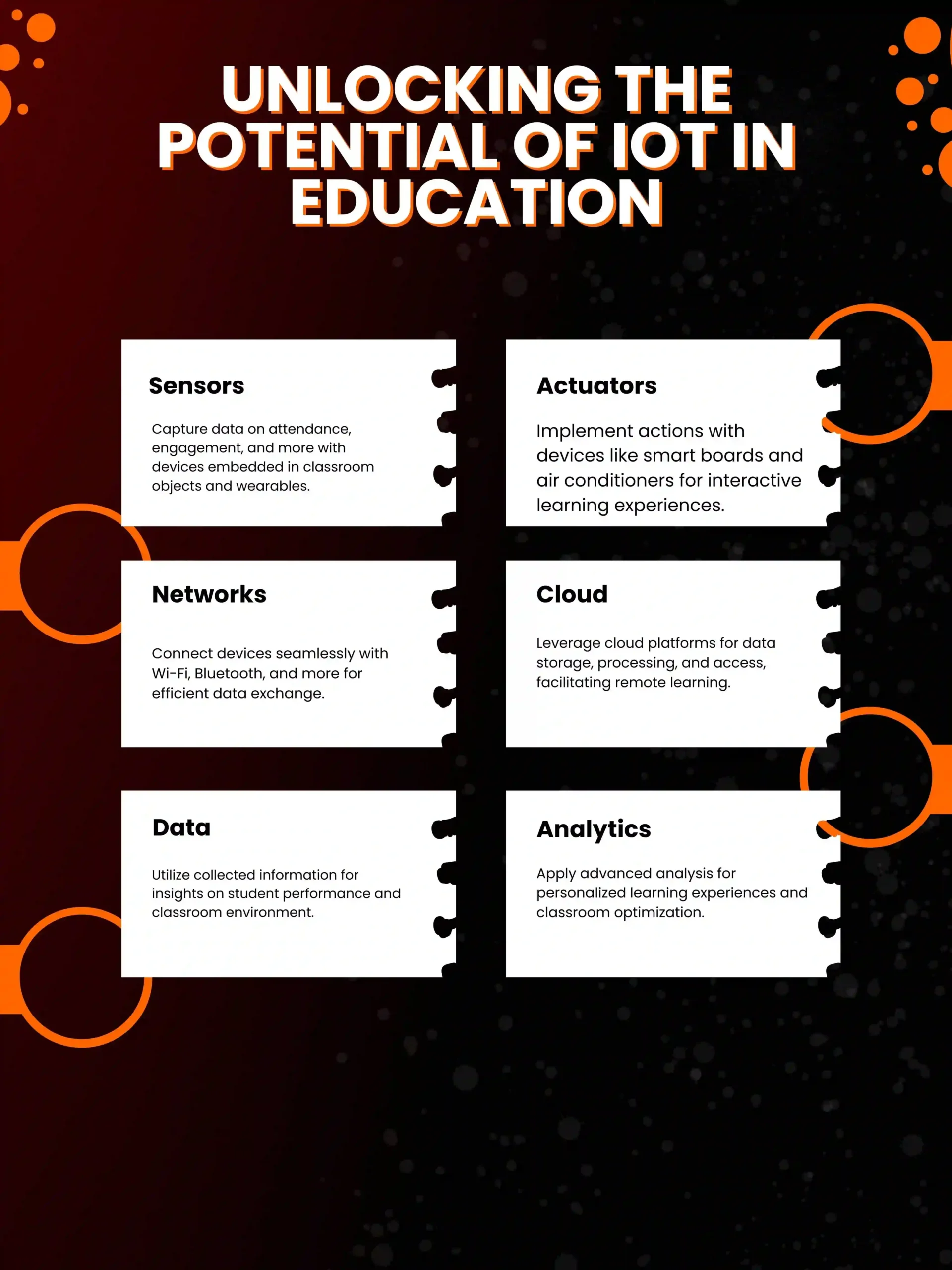
The IoT classroom works by using a combination of sensors, actuators, networks, cloud computing, data, and analytics to support learning and teaching. Here is a simplified overview of how the IoT classroom works:
Sensors
Sensors are devices that can detect and measure physical phenomena, such as temperature, light, sound, motion, and location.
Sensors can be embedded in various objects and environments, such as desks, chairs, walls, doors, windows, and floors, as well as wearable devices, such as smart watches, bracelets, and glasses.
Sensors can collect data about the state and activity of students, teachers, and the classroom, such as attendance, engagement, mood, performance, and feedback.
Actuators
Actuators are devices that can perform actions or movements based on commands or signals, such as motors, speakers, lights, and fans.
Actuators can be embedded in various objects and environments, such as smart boards, projectors, screens, and air conditioners, as well as wearable devices, such as headphones, earphones, and haptic gloves.
Actuators can provide feedback and guidance to students and teachers, such as instructions, reminders, alerts, and rewards.
Networks
Networks are systems that can connect and communicate with other devices and systems, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and cellular networks.
Networks can enable data transmission and exchange between sensors, actuators, and other devices and systems, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and servers.
Cloud
A cloud is a platform that can provide storage, processing, and access to data and applications over the internet, such as Google Cloud, Amazon Web Services, and Microsoft Azure.
The cloud can enable data aggregation, integration, and analysis, as well as application hosting, delivery, and management, for the IoT classroom.
Data
Data is the information that is collected, processed, and used by the IoT classroom, such as student and teacher profiles, preferences, behavior, engagement, performance, and feedback, as well as classroom environment, context, and content.
Data can be structured or unstructured and can be stored, retrieved, and manipulated by various databases and tools, such as SQL, NoSQL, and Hadoop.
Analytics
Analytics is the process and technique of applying statistics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to data to generate insights, predictions, and recommendations for the IoT classroom, such as student and teacher progress, outcomes, and improvement, as well as classroom optimization, personalization, and adaptation.
Analytics can be descriptive, predictive, or prescriptive and can be visualized and presented by various dashboards and reports, such as Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio.
To implement and manage the IoT classroom effectively and efficiently, here are some best practices and tips to follow:
Choose appropriate devices
The IoT classroom requires a variety of devices to function, such as sensors, actuators, networks, and the cloud. It is important to choose devices that are suitable for the learning objectives, content, and activities, as well as the classroom size, layout, and infrastructure.
It is also important to choose devices that are reliable, compatible, and interoperable, as well as easy to use, maintain, and update.
Ensure security and privacy
The IoT classroom involves a large amount of data that may be sensitive and personal, such as biometric, behavioral, and academic data. It is essential to ensure that the data is protected and secured from unauthorized access, use, and disclosure, as well as accidental loss, damage, or corruption.
It is also essential to ensure that the data is collected, processed, and shared in compliance with the relevant laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA).
It is also advisable to obtain consent and inform students and teachers about the purpose, scope, and benefits of the IoT classroom, as well as their rights and responsibilities regarding data protection and privacy.
Involve stakeholders
The IoT classroom is a complex and collaborative system that involves various stakeholders, such as students, teachers, parents, administrators, developers, and vendors.
It is important to involve and engage stakeholders in the planning, implementation, and management of IoT classrooms, as well as the evaluation and improvement of IoT classrooms.
Provide training and support to stakeholders, especially students and teachers, on how to use and benefit from the IoT classroom, as well as how to troubleshoot and resolve issues that may arise.
IoT Classroom: What Are the Examples and Applications?
The IoT classroom has many examples and applications in different subjects, levels, and contexts. Here are some of them:
Interactive whiteboards
Interactive whiteboards transform the way digital content is displayed and controlled, featuring a large touch-sensitive screen.
These devices enrich learning presentations with images, videos, animations, and slides. Beyond merely presenting content, they support collaborative and imaginative activities like brainstorming, mind mapping, and drawing.
Connectivity is another hallmark, as they can link with smartphones, tablets, laptops, and cloud services for seamless data sharing and synchronization.
Smart attendance
Utilizing IoT devices and technologies, smart attendance systems revolutionize the tracking of student and teacher presence in the classroom.
This automation extends to leveraging RFID tags, biometric scanners, facial recognition, and GPS for identification purposes.
Not only does the system ensure accurate attendance records, but it also sends alerts and notifications regarding absences or tardiness, facilitating better management and communication.
Adaptive learning
By offering tailored learning experiences, adaptive learning systems meet individual student needs, preferences, and performance levels.
This personalization is achieved through data collected via sensors, wearables, and cloud technologies, which monitor student behavior, engagement, and achievement.
Furthermore, these systems employ artificial intelligence and machine learning to adapt content and feedback dynamically, providing questions, exercises, and explanations customized to each learner’s journey.
Immersive learning
Immersive learning systems engage students with lifelike learning experiences through the use of virtual, augmented, and mixed reality technologies.
Headsets, glasses, gloves, and cameras are among the tools employed to craft vivid learning environments, from simulations to interactive scenarios.
Additionally, these experiences are made interactive through the integration of sensors, actuators, and cloud computing, enabling real-time feedback and interaction within these immersive settings.
Gamification
Gamification is a system that can apply game elements and mechanics to learning activities to increase motivation, interest, and fun.
Gamification can use various IoT devices and technologies, such as sensors, actuators, and the cloud, to create and implement gamified learning activities, such as quizzes, puzzles, and challenges.
Gamification can also use data and analytics to provide gamified feedback and rewards, such as scores, badges, and leaderboards.
There are many resources and tools available for finding and creating IoT classroom solutions. Here are some of them:
- IoT in Education: A Complete Guide: A comprehensive guide that covers the basics, benefits, challenges, and examples of IoT in education.
- IoT Classroom: A Project-Based Learning Platform: A project-based learning platform that provides IoT kits, curriculum, and support for students and teachers to create IoT projects in the classroom.
- IoT for Education: A Collection of Resources: A collection of resources, such as articles, videos, podcasts, and courses, that explore the applications and implications of IoT for education.
- IoT Education: A List of IoT Devices for Education: A list of IoT devices, such as sensors, actuators, and wearables, that can be used for educational purposes.
Conclusion
Incorporating IoT devices and solutions, the IoT classroom emerges as a dynamic learning environment, designed to significantly enhance both teaching and student engagement.
This innovative approach not only improves learning outcomes but also fosters a highly engaging, personalized, and collaborative educational experience.
It supports a wide array of activities, including the use of interactive whiteboards, implementation of smart attendance systems, adoption of adaptive learning techniques, immersion in virtual environments, and engagement in gamified learning.
Despite its numerous advantages, the transition to an IoT-enabled educational setting is not without its hurdles. Issues such as financial investment, cybersecurity, data privacy, and ethical considerations necessitate meticulous planning, execution, and ongoing management, alongside a commitment to fostering awareness, education, and regulatory compliance.
As we look towards the future, the IoT classroom stands out as a transformative force in education, promising to redefine our approach to learning and teaching.
Through this post, we aim to inspire and inform educators and learners alike about the potential benefits and applications of this technology.
Your thoughts, experiences, and queries about integrating IoT into educational spaces are highly valued. Engage with us in the comments section below to further this exciting conversation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an IoT Classroom and how does it work?
IoT Classroom is a learning environment that uses IoT devices and solutions to enhance the learning experience for students and teachers. It works by using sensors, actuators, networks, the cloud, data, and analytics to collect, process, and use data to support learning and teaching.
What are the benefits of the IoT Classroom for students and teachers?
The IoT Classroom can provide various benefits, such as enhancing learning outcomes, increasing engagement, facilitating personalization, promoting collaboration, and improving feedback. IoT Classroom can also support various learning activities, such as interactive whiteboards, smart attendance, adaptive learning, immersive learning, and gamification.
What are the challenges and limitations of the IoT classroom?
The IoT classroom also faces some challenges and limitations, such as cost, security, privacy, and ethics. IoT Classroom requires a significant investment in infrastructure, devices, software, and maintenance. IoT classrooms also pose a high risk of cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access. IoT Classroom also involves the collection, processing, and sharing of large amounts of personal and sensitive data, which may raise ethical and legal concerns.
How do you implement and manage the IoT classroom effectively and efficiently?
The IoT classroom requires careful planning, implementation, and management, as well as awareness, education, and regulation. Some best practices and tips are to choose appropriate devices, ensure security and privacy, involve stakeholders, and provide training and support.
What are some examples and applications of the IoT Classroom?
The IoT Classroom has many examples and applications in different subjects, levels, and contexts. Some of them are interactive whiteboards, smart attendance, adaptive learning, immersive learning, and gamification. There are also many resources and tools available for finding and creating IoT classroom solutions.








Recent Comments